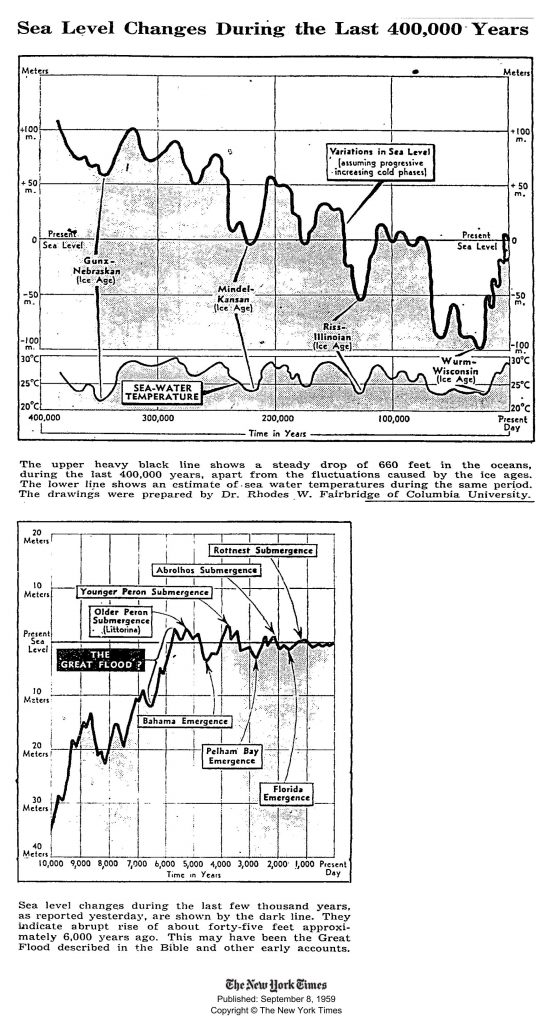
This is from the New York times in 1959.
thanks to Janet Grau for the lead!

This is from the New York times in 1959.
thanks to Janet Grau for the lead!
Continental Shelf Station was an attempt at creating an environment in which people could live and work on the sea floor. Precontinent has been used to describe the set of projects to build an underwater “village” carried out by Jacques-Yves Cousteau and his team in the Mediterranean and the Red Sea between 1961 and 1963. The projects were named Precontinent I, Precontinent II and Precontinent III. Particularly Precontinent II off the Sudanese coast received wide public recognition and was documented in a movie with the somewhat sensationalist yet eerie title “World without sun“. For a good overview of the project see: https://www.closed-worlds.com/conshelf-ii-iii or https://www.messynessychic.com/2013/05/27/remains-of-an-underwater-habitat-left-by-1960s-sea-dwellers


thanks to Lajos Talamonti for the lead!
The british movie “Captain Nemo and the underwater city” by James Hill picks up the themes and main character Captain Nemo from Jules Verne’s famous novel and the sucessfull 1954 Disney movie on the same material. While the earlier US-movie develops further the theme of the Atomic Age and it’s promises and dangers, the 1969 movie focuses on the idea of alternative, egalitarian communities and the then popular dome structures (gedesic dome) in architecture, the Montreal Biosphere built by Buckminster Fuller in 1967 being maybe the most influential and notable expample.


Each movie thus reflects the topics of it’s time. While the 1954 version is stylistically much closer to a Fin de Siecle, 19. Century aesthetic, the 1969 movie is all 60’s glitz and extravaganza. Furthermore, in the 1969 movie life under water seems like a perfectly sane and technically achievable project, while in 1954 Captain Nemo still clings on to life on land.
This is a fundamental not only technical but also political shift: The idea of leaving the known world behind, going up in space or down into the sea or exiling yourself in an alternative community is now fully developed. The Apollo Program that brought humans into space ran from 1968 to 1972. And in 1963 Jacques Cousteau constructed an underwater station where he stayed with a team of scientists for 30 days. The civilized world had thus become one of several options.

While the screen shot above shows a view of a complete city, it remains the only moment in the movie when the underwater city is actually seen. The action almost exclusively takes place in the rooms of Captain Nemo and in a swimming pool leisure area that looks more like it was directly taken from Blake Edward’s Hollywood satire “The Party” from one year earlier than like anything resembling a city. No houses, no streets, no stores or any other features of an urban environment are depicted.
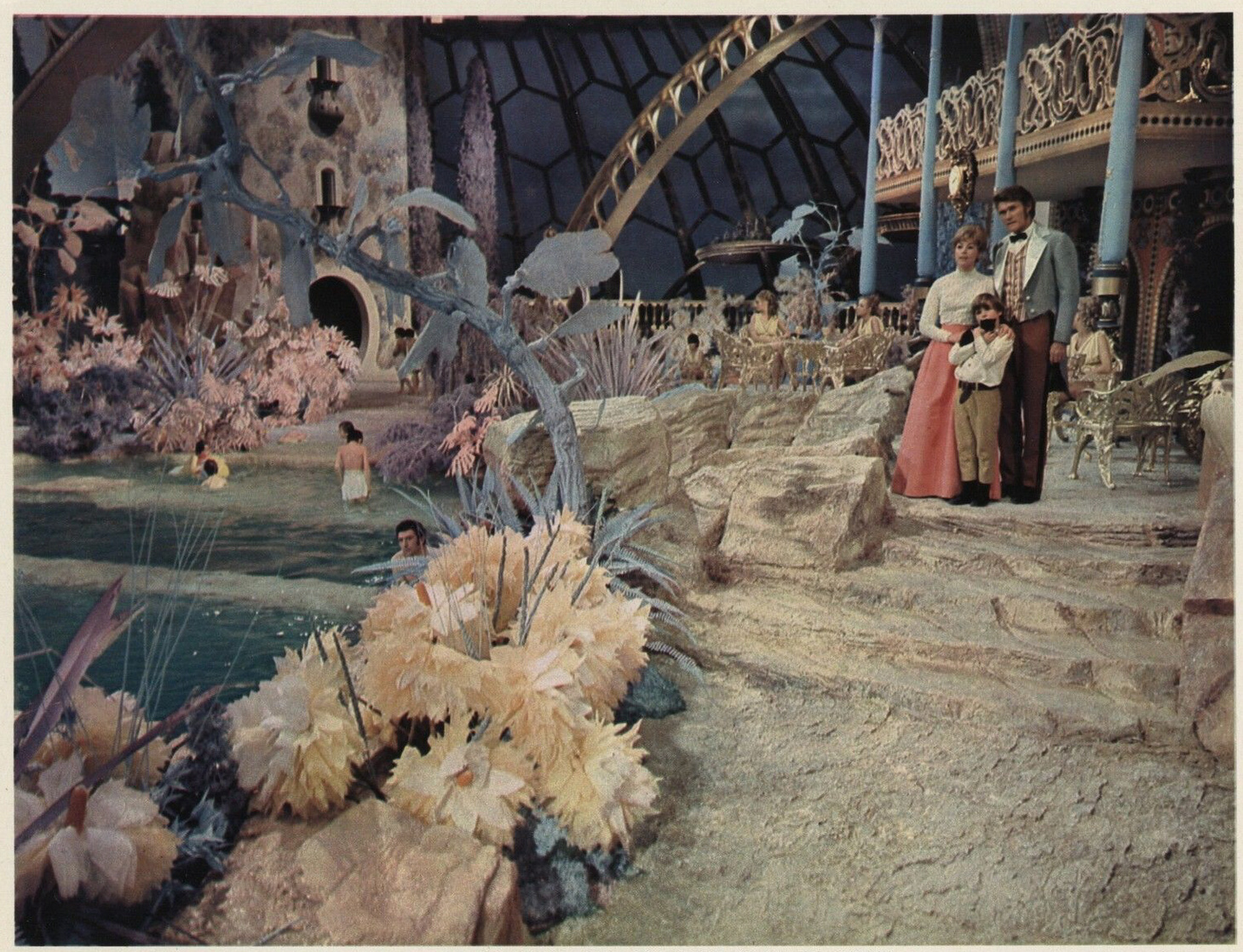

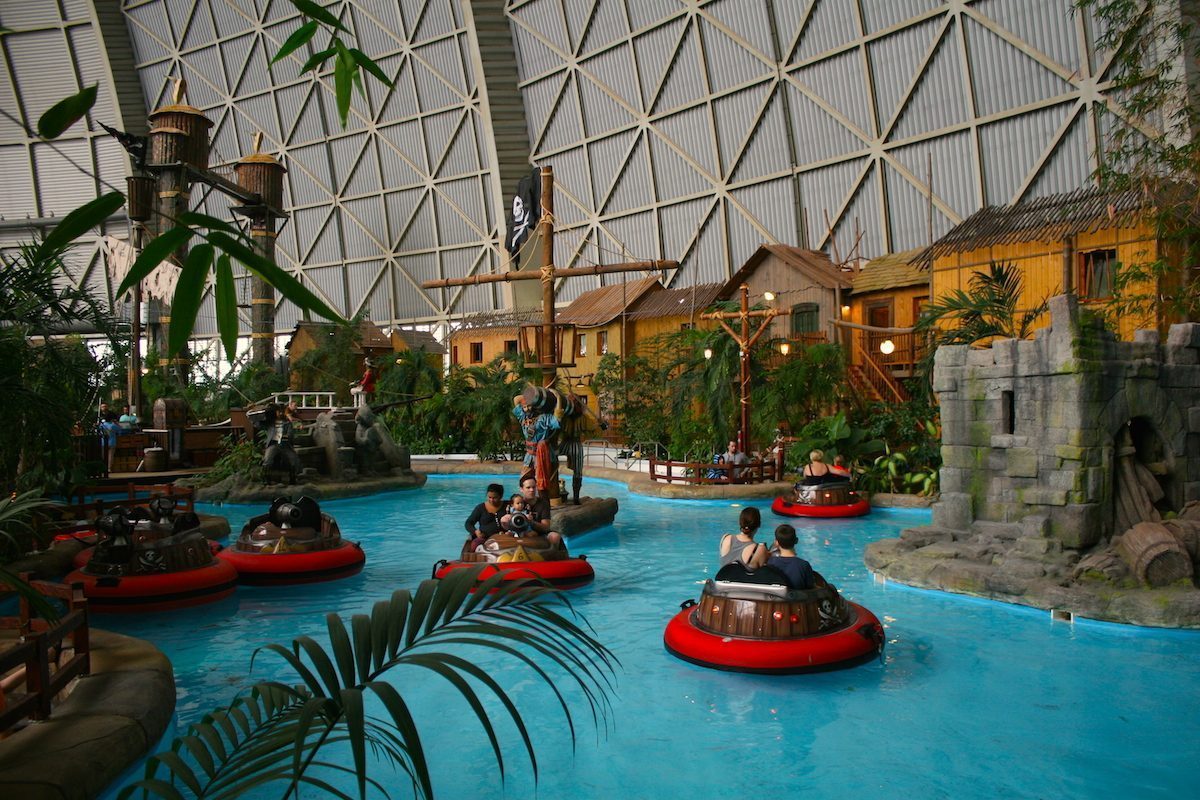
It seems that the city as a theme and topography of movies did not play a big role in the 1960’s, quite to the opposite of the era of pre-war cinema. (Take for example “Metropolis” from 1927 about another model city run by a benevolent autocrat. See my post here) . The same mixture of artificial wilderness, tropical allure and wild west or pirate movie elements, all covered by a huge dome, can also be found in today’s indoor water parks like Tropical Island near Berlin:

In the Donald Duck story “Zio Paperone e la deriva dei monumenti“ by Italian comic artists Giorgio Pezzin and Giorgio Cavazzano, Uncle Scrooge together with Donald and his nephews Huey, Dewey, and Louie save the historic buildings of Venice from rising floods.

The story first appeared as early as 1977 and has all the ingredients of our current debates about the protection of cultural heritage from climate change. Uncle Scrooge suggests to put the historic buildings on large floating pillows that would rise with the flood and lower again when the waters receed. The story was published in over a dozen countries, the german version alone saw 6 reprints until 2013.
The following images are from a German edition:
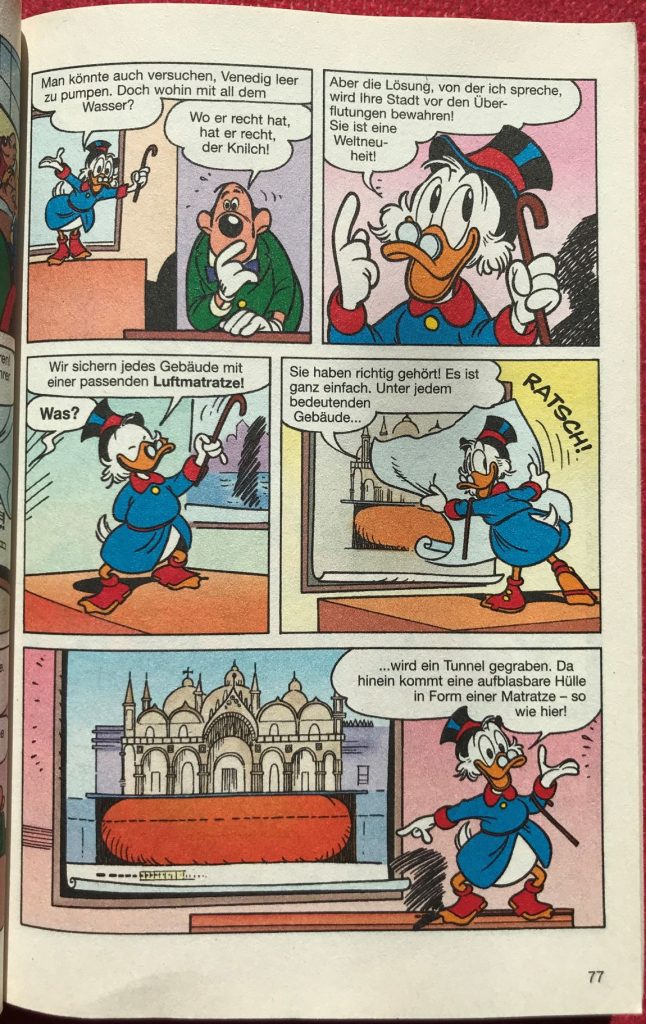



Thanks to Tobias Bulang and Janet Grau for the lead and their kid’s comic book.
“At the beginning of time, the surface of the Earth was primeval ocean where this great serpent swam or lay. The daughter of the highest deity (who dwelt in the heavens and had birds as servants) came down from the upper realm and spread a handful of earth to form the world. The serpent, however, disliked the weight upon his head, and, turning over, caused this newly made world to be engulfed by the sea.”
A folktale from Indonesia.
from: Dixon, R. B. Oceanic Mythology, Cooper Square Publishers, New York. (1916)
http://www.sacred-texts.com/pac/om/om16.htm
It might be time for a clarification. Since flood myths play quite a big role in cristian creationist ideology and since there is a lot of material online on the subject hosted on creatonist propaganda websites, I feel I need to distance myself from the creationist idoelogy once and for all. I am arguing in this blog that mythology and folklore are aesthetic reflections of natural events like tsunamis, high tides or other extreme weather phenomena. In othe words, most myths are most likely creative renditions of lived experience. This does however not mean that myths are true or – for that matter – that the bible is right. In fact I am opposed to any creationist ideology, particularly of the US-American Christian ultra-right, and fundamentally opposed to the idea of founding ethical codes of conduct on religious authority.
Having said that much, here is an online source of a chapter from Sir James George Frazer‘s book “Folk-Lore in the Old Testament” from 1918. (On a creationist website…)
The Scotish scientist Frazer is one of the founding fathers of anthropology and his study “The Golden Bough” (1928) became one of the most influential and popular texts in anthropology.
This is the section from “Folk-Lore in the Old Testament” on the flood myth. In it he gives a very detailed account of several flood myths from all continents:
https://creationism.org/books/FrazerFolkloreOT/FrazerFolkloreOT_4.htm
In this 1936 classic Sci-Fi novel (english title: The Drowned Cities), Romanian author Felix Aderca describes a future, when global cooling has forced humans to flee the Earth’s surface, rebuilding civilization on the seafloor, accessing the heat of the inner core. Here are some quotes from the German edition, describing the nearing end of the submarine citites:
„Mit unfehlbarem Instinkt begannen die Einwohner das nahende Ende zu fühlen. Ihr Arbeitsvermögen nahm rasch ab. Die Aufmerksamkeit ließ nach und die unsinnigsten tödlichen Unfälle häuften sich. Die Leute verunglückten unter unglaublichen Umständen. Es wurden sogar bei dem Bewetterungsdienst Tote gefunden, wo die Leute nur zwei automatische Metalschleusen zu überwachen hatten. Wie es hier zu tödlichen Unfällen kam, konnte niemals geklärt werden. In den Werkstätten und Laboratorien mit großen Arbeitsgruppen bewegten sich die Menschen kolonnenweise. Die einzelnen Menschen trugen kleine Lämpchen an der Stirn und, um in der Dunkelheit lastenschleppend nicht aufeinanderzuprallen, warnten sie Entgegenkommende mit langgezogenen UUU-Rufen, als seien sie im Nebel kreuzende Schiffe.“
„Die vier Städte am Meeresboden, von denen nur eine einen schwachen Lichtschimmer aussandte, schwangen in der Stille der Wassermassen wie tonlose Gongs. Haie, Stachelrochen und Polypen warteten geduldig das Ende ab.“
english google translation:
“With unerring instinct, the inhabitants began to sense the approaching end. Her ability to work declined rapidly. Attention waned and the most senseless fatal accidents began to pile up. People crashed under unbelievable circumstances. Dead bodies were even found at the ventilation service, where people only had two automatic metal airlocks to monitor. How fatal accidents happened here has never been clarified. In the workshops and laboratories with large working groups, people moved in columns. The individual people wore small lamps on their foreheads and, so as not to crash into each other in the dark, carrying loads, they warned oncoming people with long drawn-out UUU calls, as if they were ships crossing in the fog.” “The four cities at the bottom of the sea, only one of which emitted a faint glimmer of light, rang like soundless gongs in the stillness of the waters. Sharks, stingrays and polyps patiently awaited the end.”
Pak Permadi, an Indonesian expert for paranormal
events from Java made the following statement at a seminar at Jogjakarta University in 1995: »If people are not happy with their treatment by those in power but cannot defend themselves, their anger, which expresses itself as energy, is taken up by nature. If nature is angry, disasters such as a volcanic eruption occur because nature is not afraid of human rulers.«
In this oppinion, an animated nature or deity does not cause disasters directly and intentionally to comment, punish or influence human vices, but rather nature is the transmitor of a human justice. Interestingly enough, this view resonates with current climate change discourse, wherein it is human behaviour that has cuased nature to react in disastrous ways.
See: Hans-Rudolf Meier, The Cultural Heritage of the Natural Disaster: Learning Processes and Projections from the Deluge to the »Live« Disaster on TV (2007) and Judith Schlehe, Cultural Politics of Natural Disasters in Indonesia (2008)
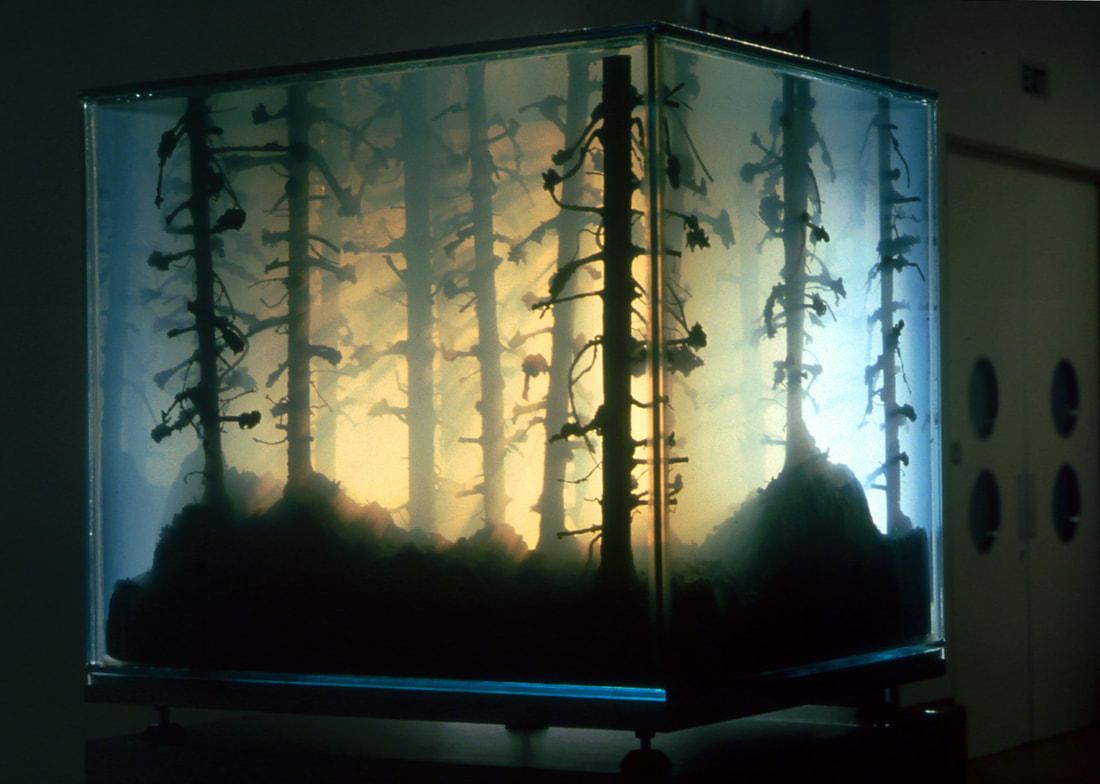

German born and UK based visual artist Mariele Neudecker creates aquarium installations of forests, houses or vessels since the late 1990’s. Her so called “tank works” are three dimensional landscapes that evoque German romanticism, scientific artefacts as well as the threat of climate change. They seem to unite past and future.
Thanks to Ingo Schöningh for the lead.
Divine punishment is an ever recuring theme in urban disasters. However, sometimes the situation does not quite fit the morals. In 1906 an earth quake hit the San Franscisco region. Fires broke out in the city, 3.000 citizens lost their lifes and 80% of the city’s buildings were destroyed. One of the buildings that were saved was the warehouse of Hotaling & Co., a local liqour company. Hotaling printed a postcard with the image below on one side and this short poem on the other:
If, as they say, God spanked the town
Because it was so frisky,
Why did he burn the churches down,
And saved Hotaling’s whiskey?
