According to historian Terje Tvedt the Greek god and hero Heracles derived from a much older Egyptian hero of similar name. The now submerged city Heracleion off the coast of the Nile delta was named after the god and Heracles plays a central role in the ancient literature of the region. The historian Diodorus of Sicily, who lived in the 1st. Century BCE, recounts Heracles’ story in detail. Among the many feats he describes, several are connected to hydrology. The most famous one is of course from the Twelve Labors of Heracles. Here is the original passage from Diodorus’ History:
“He received a Command from Eurystheus to cleanse the stables of Augeas, and to do this without the assistance of any other man. These stables contained an enormous mass of dung which had accumulated over a great period, and it was a spirit of insult which induced Eurystheus to lay upon him the command to clean out this dung. Heracles declined as unworthy of him to carry this out upon his shoulders, in order to avoid the disgrace which would follow upon the insulting command; and so, turning the course of the Alpheius river, as it is called, into the stables and cleansing them by means of the stream, he accomplished Labour in a single day, and without suffering any insult.”
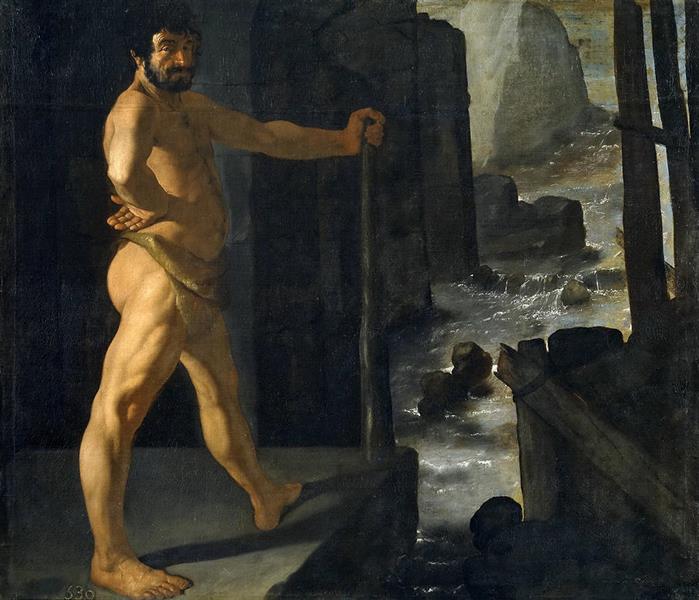

The story is reminiscent of the way ancient Egyptian society used the annual floods of the river Nile to fertilize but also clean the farm land along the river banks.
Here are two other hydraulic engineering feats:
“When Heracles arrived at the farthest points of the continents of Libya and Europe which lie upon the ocean, he decided to set up these pillars to commemorate his campaign. And since he wished to leave upon the ocean a monument which would be had in everlasting remembrance, he built out both the promontories, they say, to a great distance; consequently, whereas before that time a great space had stood between them, he now narrowed the passage, in order that by making it shallow and narrow he might prevent the great sea-monsters from passing out of the ocean into the inner sea, and that at the same time the fame of their builder might be held in everlasting remembrance by reason of the magnitude of the structures. Some authorities, however, say just the opposite, namely, that the two continents were originally joined and that he cut a passage between them, and that by opening the passage he brought it about that the ocean was mingled with our sea. On this question, however, it will be possible for every man to think as he may please.”
“A thing very much like this he had already done in Greece. For instance, in the region which is called Tempê, where the country is like a plain and was largely covered with marshes, he cut a channel through the territory which bordered on it, and carrying off through this ditch all the water of the marsh he caused the plains to appear which are now in Thessaly along the Peneius river. But in Boeotia he did just the opposite and damming the stream which flowed near the Minyan city of Orchomenus he turned the country into a lake and caused the ruin of that whole region. But what he did in Thessaly was to confer a benefit upon the Greeks, whereas in Boeotia he was exacting punishment from those who dwelt in Minyan territory, because they had enslaved the Thebans.”